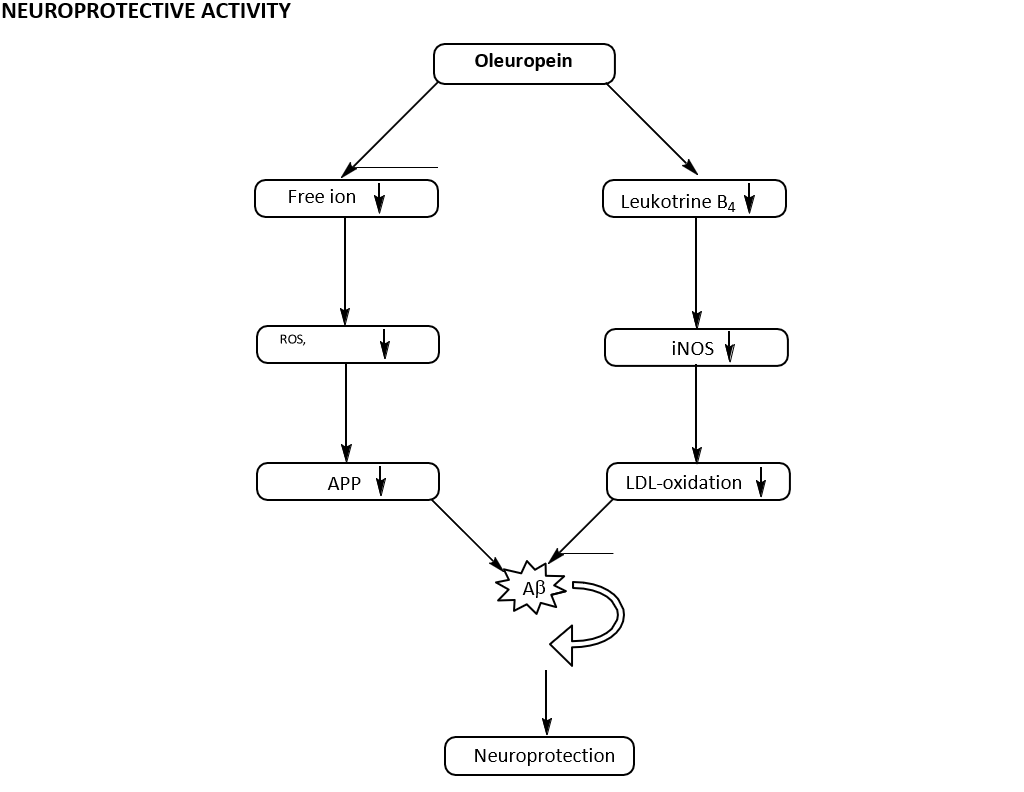
According to the free radical theory, aging is the result of oxidative injury, mainly to mitochondria, over the lifetime of an individual. Some of the oxidative damage cannot be entirely counteracted, which leads to cellular dysfunction. Mitochondrial membranes are very sensitive to free radical attack because of the presence of a double bond carbon- carbon in the lipid tails of its phospholipids, which leads to the production of cognitive and neurodegenerative disease. In vitro [1] and epidemiological [2] studies have pointed out the positive impact of natural extracted polyphenols on the incidence of age-related disorders, such as dementia. One study [3] has reported that Oleuropein decreases or even prevents Aβ aggregation, which is inherent to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The potential effect of Oleuropein on brain function in AD is analogous to atherosclerosis because they both are age-dependent diseases in which abnormal accumulation of a normal metabolite (cholesterol and Aβ, respectively) precedes clinical symptoms and leads to disease [4,5]. The link between heart disease, hypercholesterolemia, and AD [6] is due to similar mechanisms of pathogenesis of these disorders. The circumstantial evidence that cholesterol-related interventions can alter Aβ deposition [7,8] suggests that Oleuropein might be promising in the management of AD. Furthermore, the importance of inflammatory processes in the clinical manifestation of AD [9,10], combined with the epidemiological evidence of a protective effect of anti-inflammatory agents [11] against AD, suggest that a polyphenolic natural extract, such as Oleuropein, could prove effective against age-dependent disease. The diagrammatic representation of the neuroprotective role of Oleuropein is shown in Figure
-
[1] Moosmann B, Behl C.
The Antioxidant Neuroprotective Effects of Estrogens and Phenolic Compounds are Independent from their Estrogenic Properties.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999; 96: 8867–8872.
PMid:10430862
- [2] German JB, Walzem RL. The Health Benefits of Wine.
Annu Rev Nutr. 2000; 20: 561–593.
doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.20.1.561
-
[3] Bazoti FN, Bergquist J, Markides K, Tsarbopoulos A.
Noncovalent Interaction between Amyloid-β-Peptide (1– 40) and Oleuropein Studied by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry.
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2006; 17: 568–575. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2005.11.016
-
[4] Golde TE, Eckman CB.
Cholesterol Modulation as an Emerging Strategy for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Discov Today. 2001; 6: 1049–1055.
doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(01)01965-1
-
[5] Hofman A, Ott A, Breteler MM, Bots ML, Slooter AJ, van Harskamp F, van Duijn CN, Van Broeckhoven C, Grobbee DE.
Atherosclerosis, Apolipoprotein E, and Prevalence of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease in the Rotterdam Study.
Lancet. 1997; 349: 151–154. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)09328-2
-
[6] Refolo LM, Malester B, LaFrancois J, Bryant-Thomas T, Wang R, Tint GS, Sambamurti K, Duff K, Pappolla MA.
Hypercholesterolemia Accelerates the Alzheimer’s Amyloid Pathology in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Neurobiol Dis. 2000; 7: 321–331.
doi:10.1006/nbdi.2000.0304
-
[7] Refolo LM, Pappolla MA, LaFrancois J, Malester B, Schmidt SD, Thomas-Bryant T, Tint GS, Wang R, Mercken M, Petanceska SS, Duff KE.
A Cholesterol-Lowering Drug Reduces β-Amyloid Pathology in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Neurobiol Dis. 2001; 8: 890–899. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2001.0422
-
[8] Jick H, Zornberg GL, Jick SS, Seshadri S, Drachman DA. Statins and the Risk of Dementia.
Lancet. 2000; 356: 1627–1631. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03155-X
-
[9] Markesbery, WR, Carney JM.
Oxidative Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 1999; 9: 133–146. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00215.x
- [10] Heininger K.
A Unifying Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. II. Pathophysiological Processes. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp. 1999; 14: 525–581.
doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1077(199912)14:8<525::AID-HUP140>3.0.CO;2-T
- [11] Stewart WF, Kawas C, Corrada M, Metter EJ.
Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Duration of NSAID Use. Neurology. 1997; 48: 626–632.
PMid:9065537
